Settings — User Manager
The User Manager controls client access to the project's objects (which are the channels, devices, tags. etc.) and their corresponding functions. The User Manager allows permissions to be specified by user groups. For example, the User Manager can restrict the Data Client user access to project tag data based on its permissions from the Anonymous Clients user group. The User Manager can also transfer user information between server installations through its import / export function.
The User Manager has built-in groups that each contain a built-in user. The default groups are Administrators, Anonymous Clients, Server Users. The default users are Administrator, Data Client, Default User. Users cannot rename or change the description fields. Neither the default groups nor the default users can be disabled.
The User Manager has built-in groups that each contain a built-in user. The default groups are Administrators, Anonymous Clients, Server Users, and ThingWorx Interface Users. The default users are Administrator, Data Client, Default User, and ThingWorx Interface. Users cannot rename or change the description fields. Neither the default groups nor the default users can be disabled.
 Note: Although the Administrator's settings cannot be changed, additional administrative users can be added.
Note: Although the Administrator's settings cannot be changed, additional administrative users can be added.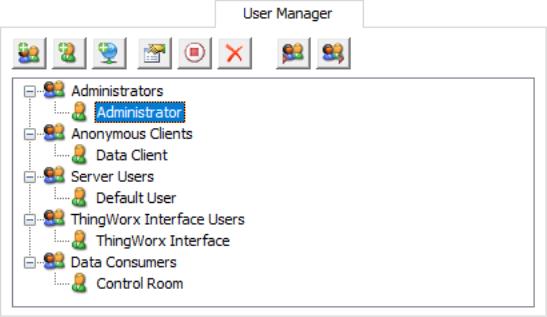
New Group: When clicked, this button adds a new Kepware Server user group. Groups cannot contain illegal characters. For more information, refer to User Group Properties.
For more information, refer to User Group Properties.
 For more information, refer to User Group Properties.
For more information, refer to User Group Properties.New User: When clicked, this button adds a new user to the selected user group. This function is disabled for anonymous clients. Users cannot contain illegal characters.
 Note: User names cannot be changed. If a user name must change, create a new user with the correct or altered name and delete the existing user. User passwords can be changed at any time.
Note: User names cannot be changed. If a user name must change, create a new user with the correct or altered name and delete the existing user. User passwords can be changed at any time. For more information, refer to User Properties.
For more information, refer to User Properties.Add AD User: When clicked, this button initiates browsing and selecting Active Directory users and groups. These users and groups are added to Kepware Server groups. Active Directory groups are configured as children to Kepware Server groups and inherit their permissions.
Edit Properties: When clicked, this button allows users to edit the properties of the selected user or user group.
 Tip: To update multiple permissions at the same time, right-click on the property group and select the desired permissions.
Tip: To update multiple permissions at the same time, right-click on the property group and select the desired permissions. 
Disable Selected User / Group: When clicked, this button disables the selected user or user group. This function is only available to custom users and user groups. Disabling a user group disables all users within it.
Restore Selected User / Group: When clicked, this button restores the selected user or user group. Restoring a user group returns the users within it to the state they were in prior to disabling. This icon is only available once a user or user group has been disabled.
Delete Selected User / Group: When clicked, this button deletes the selected user or user group. This function is only available to custom users and user groups (not users pre-configured by installation). Deleting a user group removes all users within it.
Import User Information: When clicked, this button imports user information from an XML file. For the import to succeed, the file that is selected must have been exported from the server's Administration utility. This function is only enabled when a member of the built-in Administrators group is logged in.
Export User Information: When clicked, this button exports user information to an XML file. This is useful for users that need to move the project from one machine to another. Administrators also have the option to password protect the XML file: if utilized, the correct password must be entered for the import to succeed on the new machine. The XML file cannot be edited and re-imported. This function is enabled at all times.
 The Import / Export User Information features were released in server version 5.12. Any user passwords that were set while using previous server versions must be changed in 5.12 before an export is attempted; otherwise, the export fails.
The Import / Export User Information features were released in server version 5.12. Any user passwords that were set while using previous server versions must be changed in 5.12 before an export is attempted; otherwise, the export fails. After upgrading the server or importing User Information, it is recommended to review the User Manager permissions for accuracy.
After upgrading the server or importing User Information, it is recommended to review the User Manager permissions for accuracy. Imports and upgrades from older versions may fail due to users or groups containing illegal characters. In this case, fix the names before exporting from older versions.
Imports and upgrades from older versions may fail due to users or groups containing illegal characters. In this case, fix the names before exporting from older versions. Note: Import User Information replaces existing users and user groups with those being imported (except for the Administrator built-in user).
Note: Import User Information replaces existing users and user groups with those being imported (except for the Administrator built-in user).Illegal Characters
For local server users and groups, some characters are not permitted in local server user names and local group names (Version 6.9 and higher). In particular, forward (/) and backward (\) slashes are NOT allowed. Trying to create users or groups with these characters causes a failure message that describes illegal characters.
Accessing Additional Settings
Shortcuts and additional settings may be accessed through the context menus for user groups and users.

Move User To This option moves the user to a different user group. The status of the group does not matter: both disabled and enabled groups appear in the list. An active user moved to a disabled group becomes disabled as well. A disabled user moved to an enabled group persists in status until changed.
Active Directory Users and Groups
Active Directory users and groups allow the application to utilize Windows users and groups to sign into and configure Kepware Server. Human-readable user names are displayed for users and groups whenever possible; however, SIDs are Window’s unique identifier for users and groups. If a user or group is deleted from the domain, or a domain controller cannot be found, the SID is displayed instead. This may indicate a user has been removed from the domain. Users disabled on the domain are displayed as human-readable names, but authentication with them is not possible. Authentication when reaching out to a domain controller may be slow.
Active Directory Groups: Active Directory groups can be added as children to Kepware Server groups. When attempting to sign in as a Windows user, the software determines if the user is a part of a configured Active Directory group. If so, that user signs in with the permissions of the Kepware Server group that is a parent of the configured Active Directory group. Local Windows users may be matched with local Windows groups. Distribution groups and computers cannot be configured. Service accounts are supported. Groups are not supported for real-time data interfaces.
 Note: Active Directory (AD) users granted access to the server via Active Directory Groups must be direct members of AD Groups added to the User Manager to have access to the server. Members of AD groups that are nested within AD groups added to User Manager are not supported.
Note: Active Directory (AD) users granted access to the server via Active Directory Groups must be direct members of AD Groups added to the User Manager to have access to the server. Members of AD groups that are nested within AD groups added to User Manager are not supported. Caution: Having Active Directory (AD) users in multiple configured AD groups is not recommended because the resulting permissions may be challenging to manage. If an AD user is part of multiple AD groups, only one AD group is used to determine the Kepware Server group permissions used. If an AD user is configured as part of a Kepware Server group, and the AD user is also a member of a configured AD group, the individual AD user permissions take precedence. If an AD user is not configured, but an AD group is, a login prompt is displayed to allow specific user credentials to be entered. The entered credentials are then passed to the Domain Controller for verification.
Caution: Having Active Directory (AD) users in multiple configured AD groups is not recommended because the resulting permissions may be challenging to manage. If an AD user is part of multiple AD groups, only one AD group is used to determine the Kepware Server group permissions used. If an AD user is configured as part of a Kepware Server group, and the AD user is also a member of a configured AD group, the individual AD user permissions take precedence. If an AD user is not configured, but an AD group is, a login prompt is displayed to allow specific user credentials to be entered. The entered credentials are then passed to the Domain Controller for verification. Tip: To configure Kepware Server as a standard user (non-Administrator Windows user), grant the standard user read and write privileges to the Application Data directory. Only an administrator can set these permissions.
Tip: To configure Kepware Server as a standard user (non-Administrator Windows user), grant the standard user read and write privileges to the Application Data directory. Only an administrator can set these permissions. Warning: Ensure that any domain accounts to be used are configured with domain Active Directory groups and that any local (Windows) accounts to be used are configured with local AD groups. Kepware Server does not allow the mixing of local and domain users and groups
Warning: Ensure that any domain accounts to be used are configured with domain Active Directory groups and that any local (Windows) accounts to be used are configured with local AD groups. Kepware Server does not allow the mixing of local and domain users and groups Warning: Windows 8 and 8.1 Professional editions do not support local groups built into the operating system (such as the Everyone group), but do support domain groups and local users.
Warning: Windows 8 and 8.1 Professional editions do not support local groups built into the operating system (such as the Everyone group), but do support domain groups and local users.Supported Interfaces
Active Directory user and group access is permitted in the following interfaces:
• Server Configuration GUI
• Server Administration
• Configuration API
• OPC .Net
Partially Supported Interfaces
The following interfaces support Active Directory authentication with configured users, but not configured groups:
• IoT Gateway
• OPC UA
 For additional information on how to properly supply credentials in places where Active Directory is unavailable, refer to the section below regarding the Configuration API.
For additional information on how to properly supply credentials in places where Active Directory is unavailable, refer to the section below regarding the Configuration API.Server Configuration and Administration: When launching the Server Configuration application and the Server Administration application, Kepware Server attempts to seamlessly log in as the current user on the machine prior to attempting any default users. When logging into the Server Configuration application, if a configured matching Active Directory user cannot be found (most likely because one has not been configured), an informational message is posted, and the Default User is attempted. When logging into the Server Administration application, if a matching Active Directory user cannot be found, the Administrator user is attempted. In both cases, if the server cannot successfully log in, a login prompt is displayed. If the server is configured to use Active Directory and there is a desire for a different user to log in, the recommended way to do so is to log into the windows machine as that different user.
Configuration API: When using authentication with the Configuration API service, an Active Directory user can be specified by supplying the username of [Domainname|Computername]\[Username] and the password associated with that user. The ‘\’ is used to determine if an attempted login should be treated as an Active Directory user that needs to be authenticated. The configuration API service will validate that username and password, and grant permissions based on the User Manager’s configuration. If no ‘\’ is supplied, the Configuration API will treat the username as a Kepware Server user and validate the supplied password internally.
 Note: Active Directory user passwords and names cannot be managed over the configuration API and must be changed via the operating system or domain controller on which they reside.
Note: Active Directory user passwords and names cannot be managed over the configuration API and must be changed via the operating system or domain controller on which they reside.IoT Gateway and OPC UA: Active Directory users can be specified by supplying the username of [Domainname|Computername]\[Username] and the password associated with that user. The backslash (\) is used to determine if an attempted login should be treated as an Active Directory user who needs to be authenticated. Kepware Server validates that user name and password, then grants permissions based on the User Manager’s configuration. If no backslash (\) is supplied, it treats the user name as a Kepware Server user and validates the supplied password internally.
 Note: IoT Gateway and OPC UA are only compatible with configured Active Directory users, not groups.
Note: IoT Gateway and OPC UA are only compatible with configured Active Directory users, not groups.User Group Properties
The user group properties may also be accessed by right-clicking on a user group and selecting Properties.
 Tip: To quickly allow or deny all options in a category, right-click on the category and select Allow All or Deny All. A setting that displays bold text indicates that its value has been changed. Once the change is saved, the text displays as normal.
Tip: To quickly allow or deny all options in a category, right-click on the category and select Allow All or Deny All. A setting that displays bold text indicates that its value has been changed. Once the change is saved, the text displays as normal.
Name: Click the icon to open the name of the new user group. The maximum number of characters allowed is 31. Duplicate names are not allowed.
Description: This optional property provides a brief description of the user group. This can be particularly helpful for operators creating new user accounts. The maximum number of characters allowed is 128.
Permissions assigned to this user group: This field assigns permissions for the selected user group. Permissions are organized into the following categories: Project Modification, Server Permissions, I/O Tag Access, System Tag Access, Internal Tag Access, and Browse Project Namespace. More information on the categories is as follows:
• Project Modification: This category specifies permissions that control default project modifications.
• Server Permissions: This category specifies permissions that control access to server functionality. These permissions are not supported by the anonymous client.
• I/O Tag Access: This category specifies permissions that control access to device-level I/O tag data. These tags require device communications and are described as Static tags in the server.
• System Tag Access: This category specifies permissions that control access to System tags. These tags begin with an underscore and exist in a server-defined location. For more information, refer to System Tags.
• Internal Tag Access: This category specifies permissions that control access to internal tags. These tags are either driver-managed (controlling some aspect of the driver's operation) or user-specified (at a plug-in level).
• Browse Project Namespace: This category specifies permissions that control browse access to the project namespace in clients that support browsing. This is not supported by all client types.
• Event Log: This category specifies permissions that control access to the informational, warning, error, and security messages posted to the event log. The defaults are Allow. Some clients require a runtime reinitialization for these settings to take effect. Note: When the server_config is in offline mode, the event log view uses event filtering set for the anonymous client.
Note: When the server_config is in offline mode, the event log view uses event filtering set for the anonymous client.
 Note: When the server_config is in offline mode, the event log view uses event filtering set for the anonymous client.
Note: When the server_config is in offline mode, the event log view uses event filtering set for the anonymous client. Tip: To view more information on a specific object in a category, select it.
Tip: To view more information on a specific object in a category, select it.User Properties
The user properties may be accessed by double-clicking on the user or right-clicking on the user and selecting Properties....
 Note: Active Directory user passwords and names cannot be managed here and must be changed via the operating system or domain controller on which they reside.
Note: Active Directory user passwords and names cannot be managed here and must be changed via the operating system or domain controller on which they reside.
Old Password: This field holds the password that has been active for this user.
Password: Enter a new or updated password this user must enter to log into the system. It is case-sensitive with a minimum of 14 and a maximum of 512 characters. The password must include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid well-known, easily guessed, or common passwords. Passwords greater than 512 characters will be truncated.
Confirm Password: Re-enter the same password. It must be entered exactly the same in both the New Password and Confirm Password fields.